Inquiry
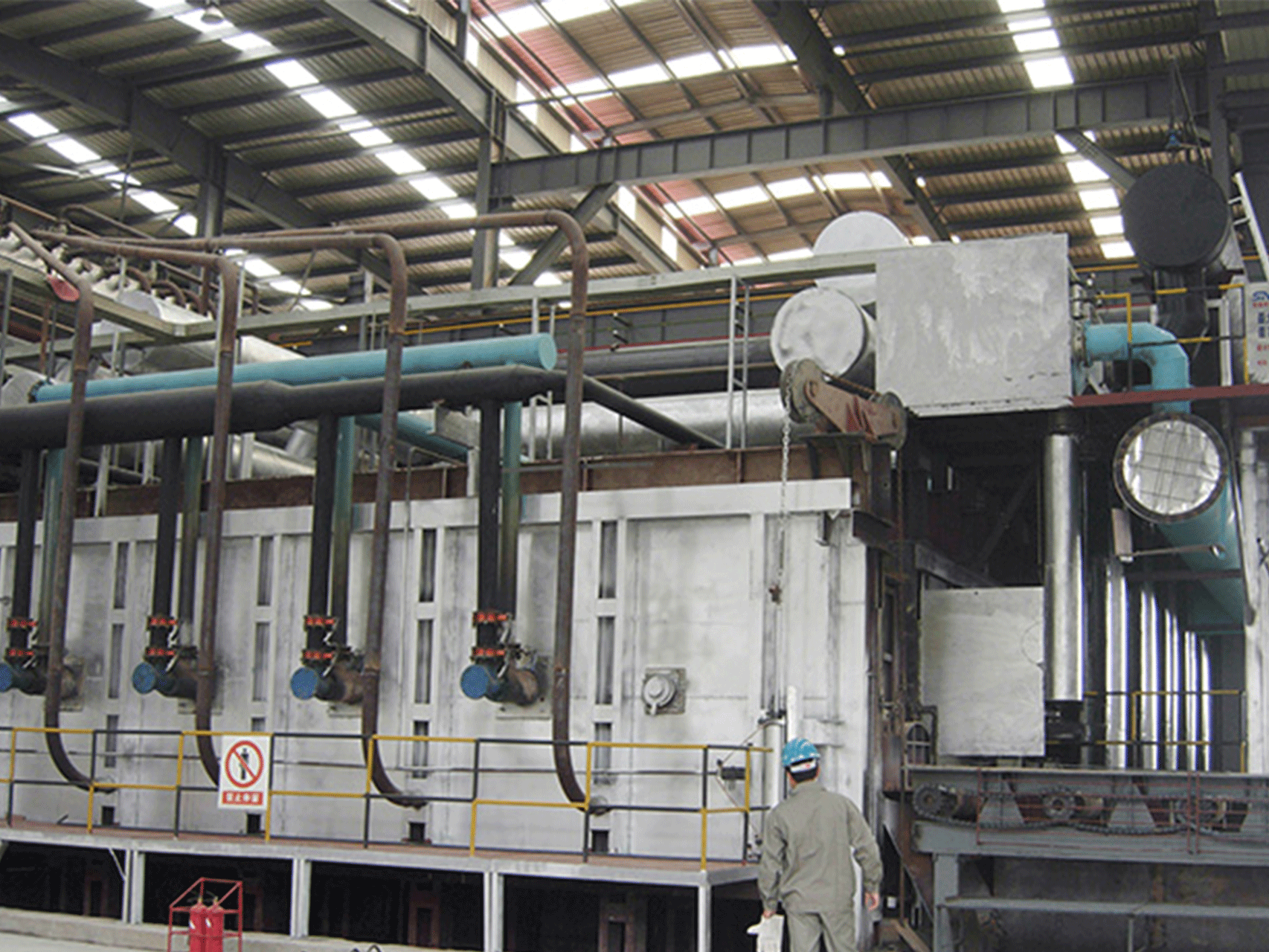
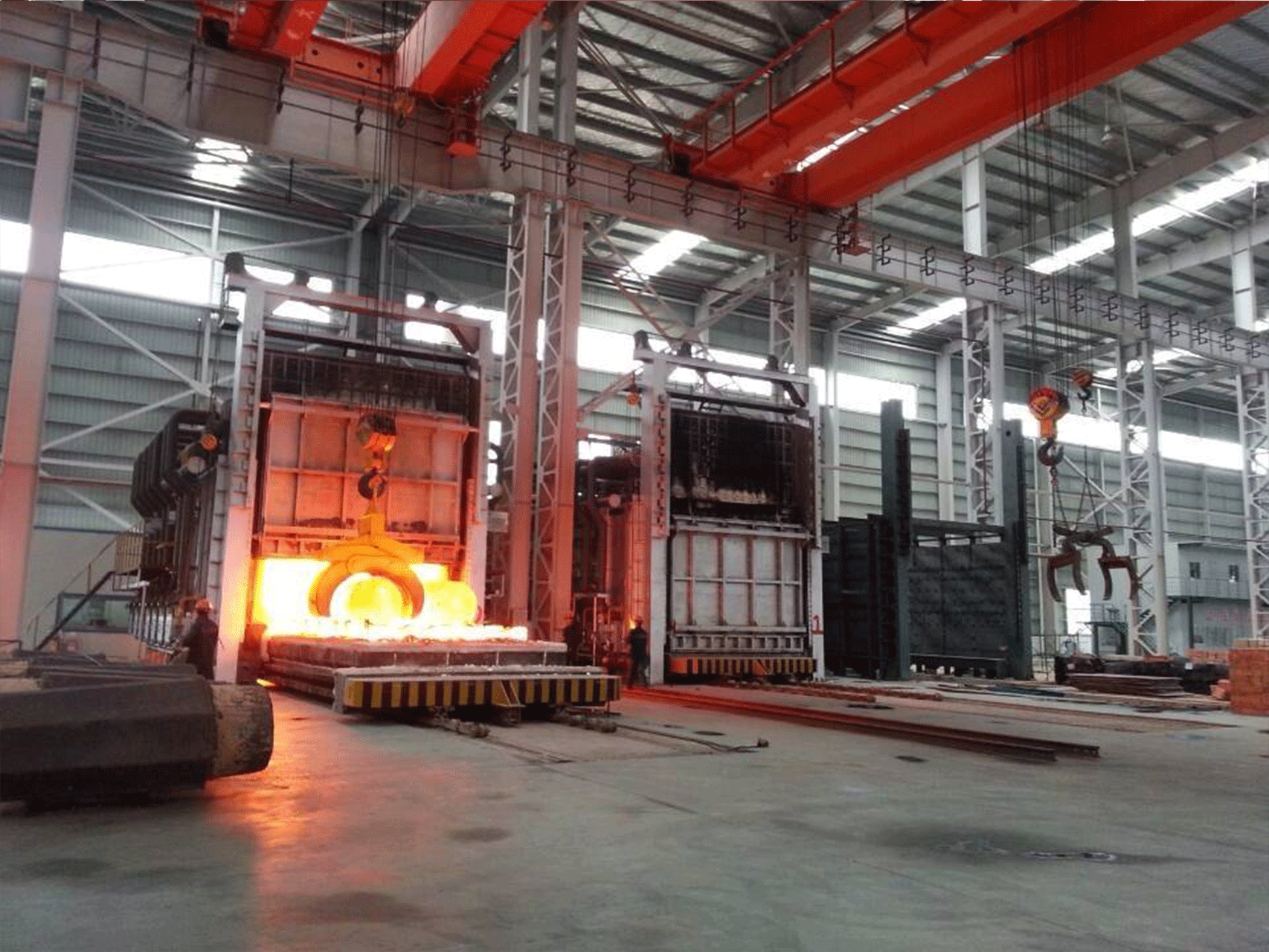
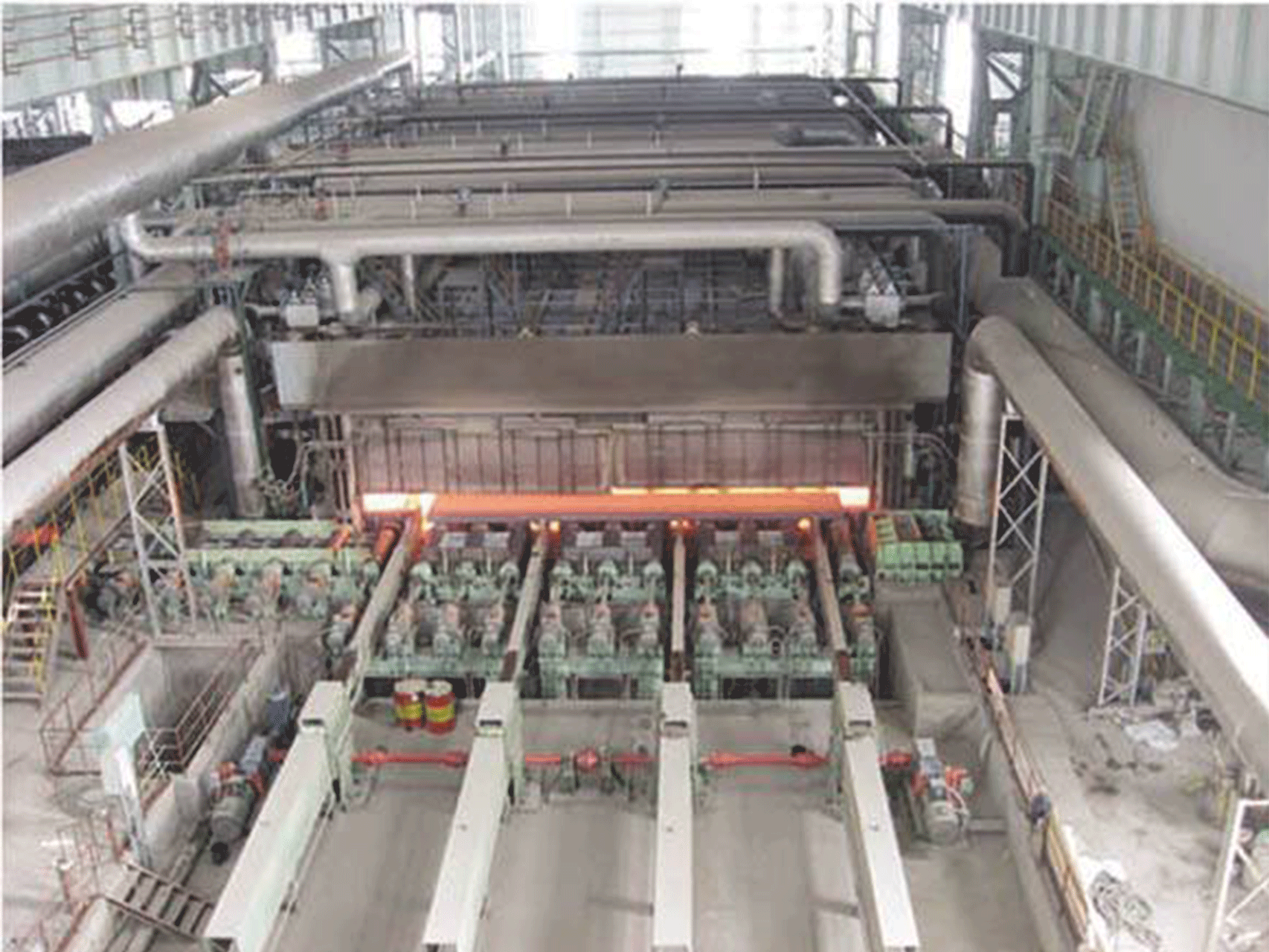
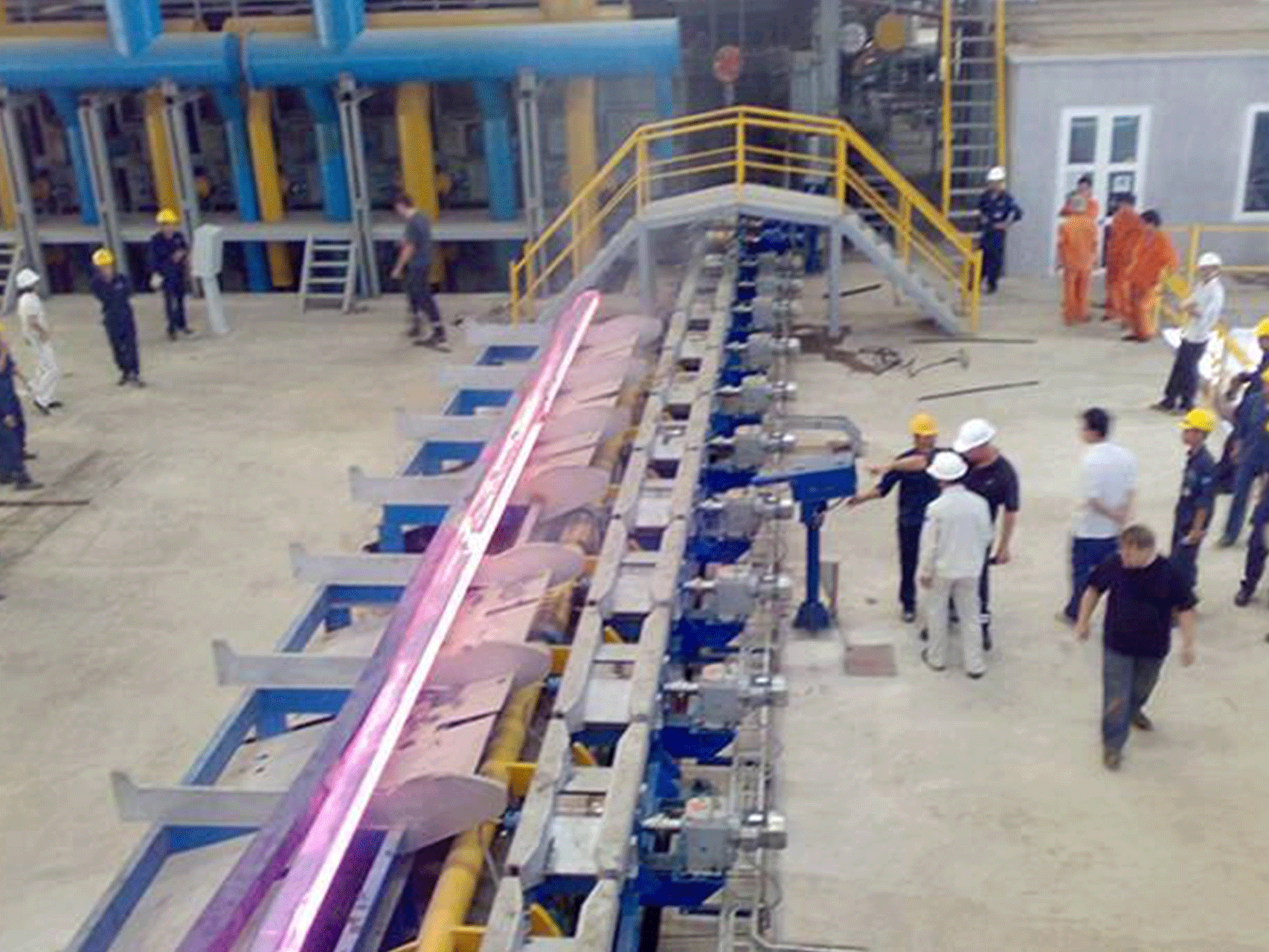
Forging furnace
A forging furnace is an industrial furnace used for heating metal to high temperatures in preparation for forging, a process in which the metal is shaped by applying compressive force. There are several types of forging furnaces, including gas-fired furnaces, electric furnaces, and induction furnaces.
Gas-fired forging furnaces typically use natural gas, propane, or other fuels to heat the metal. The furnace consists of a chamber lined with heat-resistant materials, with burners positioned at one end to produce flames that heat the metal. Gas-fired furnaces are often used in applications where large amounts of metal need to be heated quickly and efficiently.
Electric forging furnaces use electric heating elements to heat the metal. The furnace consists of a chamber lined with heat-resistant materials and one or more electric heating elements that generate heat when an electric current is passed through them. Electric furnaces are often used in applications where precise temperature control is required, or where a clean, controlled environment is necessary.
Induction forging furnaces use an electromagnetic field to heat the metal. The furnace consists of a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field, which induces electrical currents in the metal, heating it up. Induction furnaces are often used in applications where rapid heating and cooling is required, or where a high degree of precision is necessary.
Forging furnace advantage
Forging furnaces are used in industrial processes to heat and soften metals for shaping and forming. Some of the advantages of using forging furnaces include:
- Consistent heat: It can provide precise and consistent heat, allowing for more accurate control of the heating process and resulting in more uniform and predictable outcomes.
- Improved efficiency: Modern forging furnaces are designed to be highly efficient, reducing energy consumption and operating costs.
- Faster heating times: It can heat metal to high temperatures quickly, reducing the amount of time required for the forging process and increasing productivity.
- Versatility: It can be used for a variety of metalworking processes, including forging, tempering, annealing, and stress relieving.
- Reduced material waste: The precise and controlled heating provided by forging furnaces can reduce the risk of overheating or underheating metal, resulting in less material waste and improved yield.
Forging furnace FQA
- What temperature can a forging furnace reach?
The temperature a forging furnace can reach depends on the type of furnace and the materials being heated, but generally, forging furnaces can reach temperatures between 1000°C (1832°F) and 1300°C (2372°F).
- What types of fuel can be used in a forging furnace?
Different types of fuel can be used in a forging furnace, including natural gas, propane, oil, and electricity. Gas-fired furnaces typically use natural gas or propane, which are burned to generate heat. Oil-fired furnaces use heating oil, which is burned to produce heat. Electric furnaces use electric heating elements to generate heat. Induction furnaces use electromagnetic fields to heat the metal, and typically require electricity to operate.
The choice of fuel depends on factors such as the availability and cost of the fuel, the specific heating requirements of the materials being forged, and the desired level of efficiency and environmental impact. Some types of fuel may be more efficient or produce less emissions than others, so careful consideration is necessary when selecting the fuel for a forging furnace.
- How long does it take for a forging furnace to heat up?
The amount of time it takes for a forging furnace to heat up depends on several factors, including the size and type of furnace, the type and amount of fuel being used, and the initial temperature of the furnace and the materials being heated.
Generally, it takes between 1 to 2 hours to heat up to the desired temperature range for forging, which can range between 1000°C (1832°F) and 1300°C (2372°F). However, this can vary depending on the specific furnace and materials being heated.
- How long does a forging furnace last?
The lifespan can vary depending on several factors, such as the type and quality of the furnace, the frequency of use, and the specific operating conditions. With proper maintenance and care, a well-built forging furnace can last for many years. However, it's also important to note that frequent use and harsh operating conditions can shorten the lifespan of a furnace.
- Can a forging furnace be used for other heating applications besides forging?
It can be used for other heating applications besides forging, depending on its design and capabilities. For example, some types of forging furnaces can be used for heat treating, annealing, or other types of metalworking processes that require high-temperature heating. Additionally, with certain modifications, a forging furnace can be used for applications outside of the metalworking industry, such as drying or curing processes that require high-temperature heating.
- What safety precautions should be taken when operating a forging furnace?
Operating a furnace can be hazardous, and there are several safety precautions that should be taken to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. Here are some important safety precautions to consider when operating a forging furnace:
- Wear appropriate protective clothing and equipment, such as heat-resistant gloves, aprons, and face shields, to protect against burns and other injuries.
- Make sure the furnace is properly installed and maintained, and that all safety features are in place and working correctly.
- Use caution when opening or closing the furnace doors, as the heat and pressure inside can cause hot gases or molten metal to escape.
- Use appropriate ventilation and exhaust systems to prevent the buildup of hazardous fumes or gases.
- Follow proper loading and unloading procedures, and make sure the materials being heated are properly secured to prevent shifting or falling.
- Never leave the furnace unattended while it is in operation, and make sure it is shut off properly when not in use.
- Have appropriate fire extinguishing equipment nearby in case of a fire or other emergency.