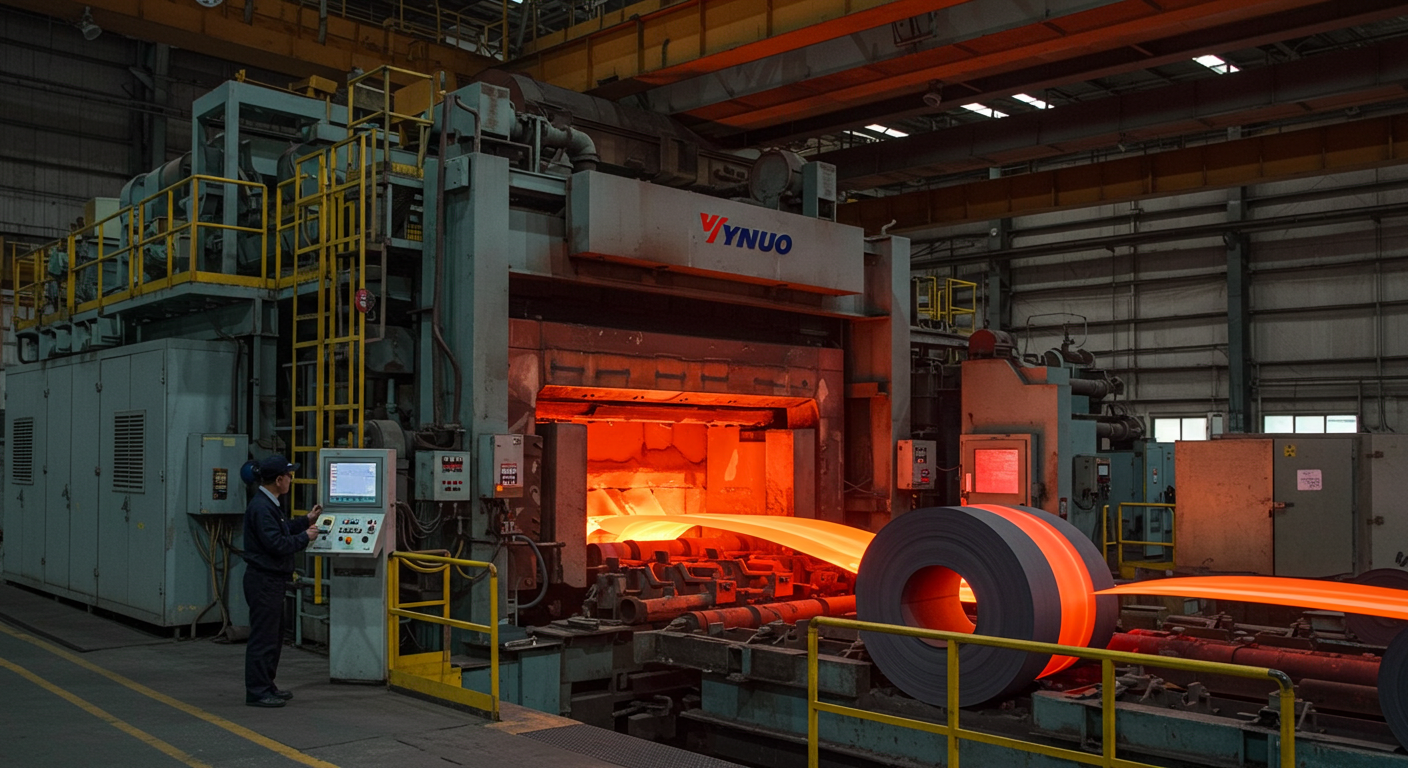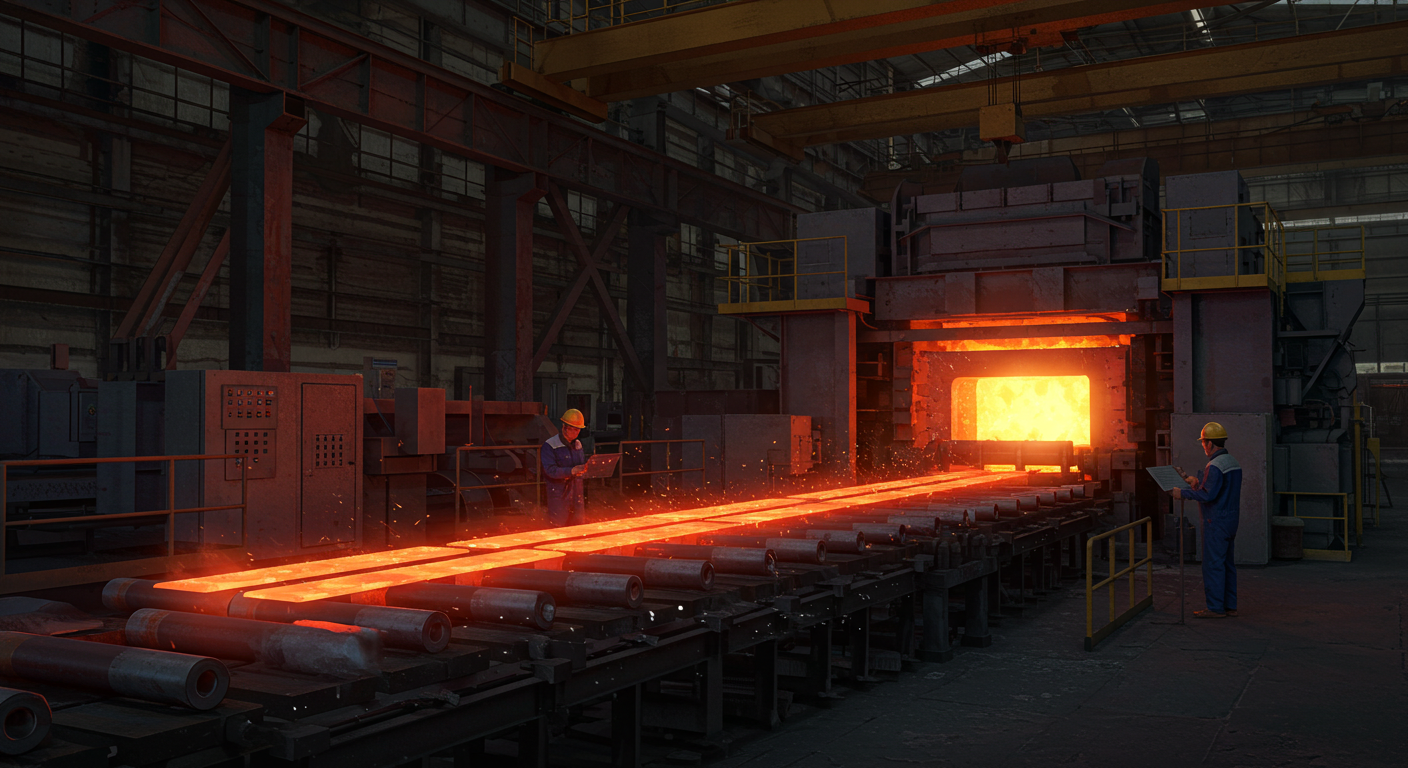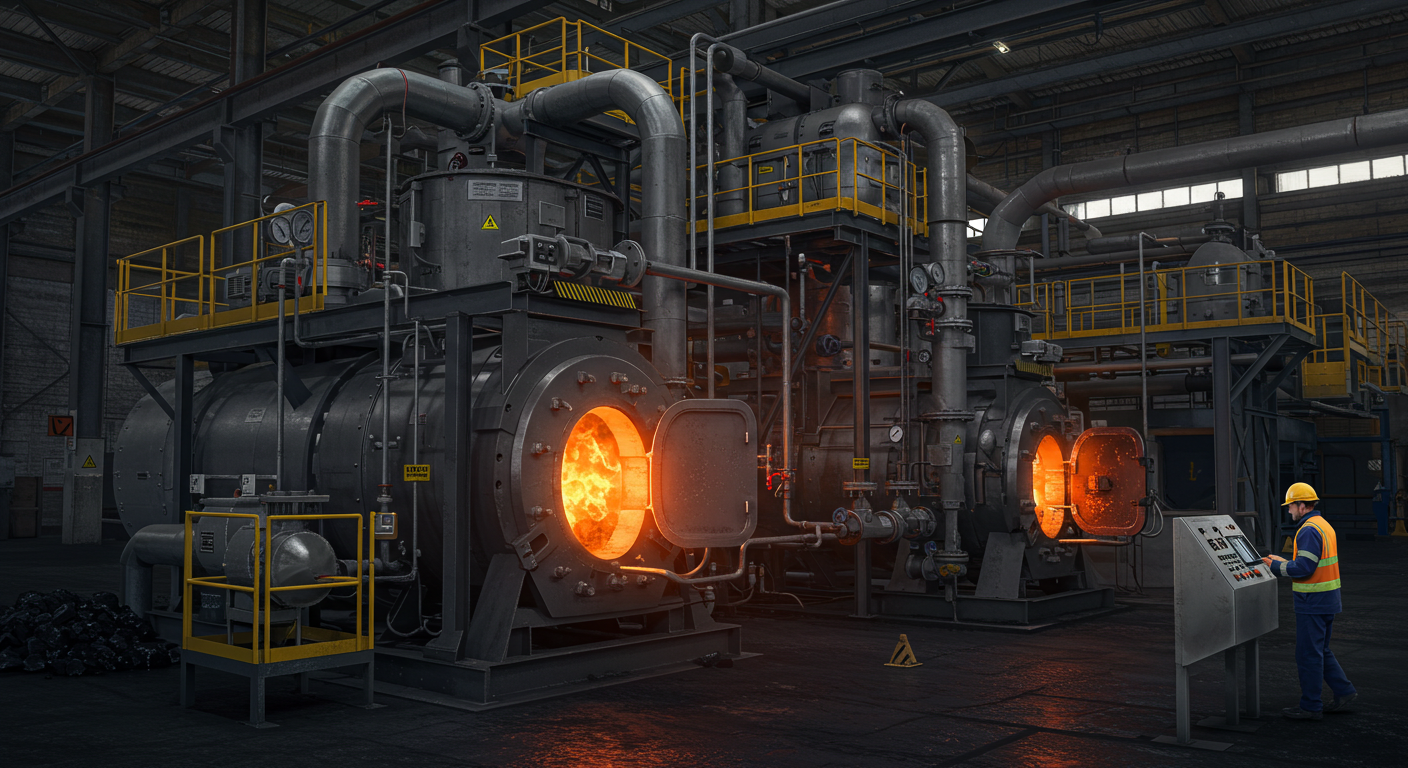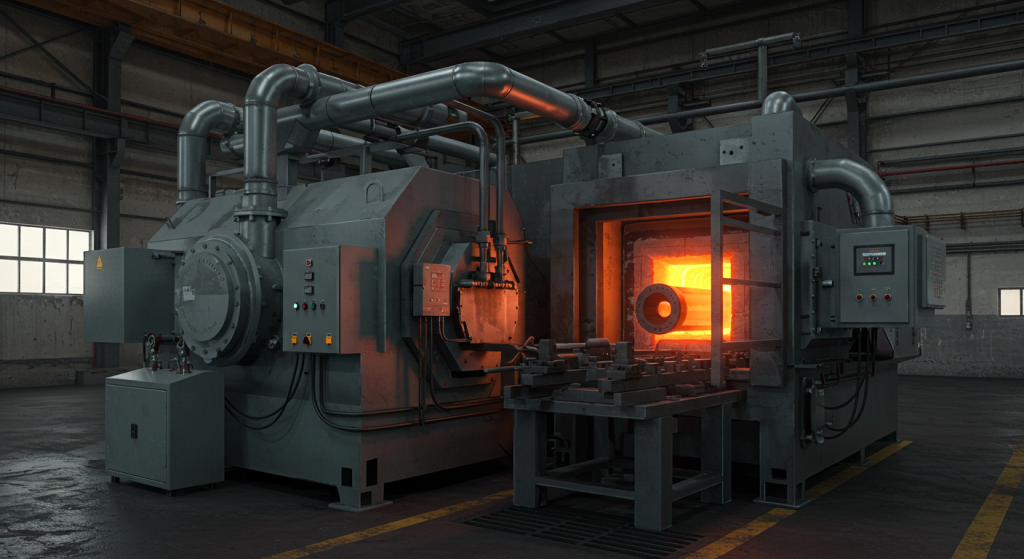
In the fast-paced world of industrial manufacturing, where precision, efficiency, and material quality define success, gas fired annealing furnaces stand as critical tools for transforming metals into high-performance components. These advanced systems leverage the energy efficiency and controllability of natural gas to deliver precise heat treatment, enabling industries like steel, aerospace, and automotive to meet stringent performance standards. At Jiangsu Yinuo Thermal Energy Technology Co., Ltd., we specialize in designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art industrial furnaces, including gas fired annealing furnaces, forging furnaces, and reheating furnaces, tailored to the needs of modern manufacturing. This 2500-word blog post, crafted for industrial engineers, maintenance technicians, and procurement managers, explores the mechanics, benefits, applications, and future of gas fired annealing furnaces. With a professional tone, internal links to hypothetical pages on our website, H3 subheadings for clarity, and a dedicated FAQ section, we highlight how Yinuo’s innovative solutions empower industries to achieve excellence.
Understanding Gas Fired Annealing Furnaces
A gas fired annealing furnace is a specialized industrial system that uses natural gas combustion to heat metals—such as steel, aluminum, copper, or specialty alloys—to specific temperatures, followed by controlled cooling to enhance material properties. The annealing process relieves internal stresses, improves ductility, refines grain structures, and enhances machinability, making it essential for producing high-quality materials. Unlike electric or induction furnaces, gas fired furnaces offer cost-effective, high-energy output, making them ideal for large-scale or continuous operations.
Core Design and Functionality
Yinuo’s gas fired annealing furnaces are engineered for both batch and continuous annealing, accommodating diverse production needs. They are critical in industries requiring consistent material properties, such as automotive sheet metal or aerospace structural components. Their ability to deliver uniform heating, precise atmosphere control, and energy efficiency sets them apart in modern manufacturing. Explore our full range of furnace solutions on our Products page.
Why Gas Fired?
Natural gas provides a reliable, high-energy heat source, offering lower operational costs compared to electric systems, especially for high-volume processes. Yinuo’s furnaces maximize this advantage with advanced burner technologies and heat recovery systems.
How Gas Fired Annealing Furnaces Operate
The operation of a gas fired annealing furnace combines thermal precision, material science, and advanced engineering. The furnace features a refractory-lined chamber where natural gas burners generate controlled heat. Metals, loaded as coils, sheets, or components, are heated to temperatures typically between 600°C and 900°C, depending on the material and annealing goals. A protective atmosphere—often nitrogen, hydrogen, or a mixture—prevents oxidation, while cooling systems, such as gas jets or water sprays, regulate the cooling rate to achieve desired properties.
Precision Control Systems
Yinuo’s furnaces are equipped with sophisticated control systems, including thermocouples, gas flow regulators, and real-time monitoring, to maintain tight temperature tolerances. These systems ensure consistency across production runs, critical for high-value applications like electrical steel or aerospace alloys. For details on our technological advancements, visit our Services page.
Energy-Efficient Mechanisms
Our furnaces incorporate regenerative burners, high-performance insulation, and waste heat recovery to minimize fuel consumption and emissions, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Benefits of Gas Fired Annealing Furnaces
Gas fired annealing furnaces offer a range of advantages that make them a preferred choice for industrial manufacturers. Their ability to deliver consistent metallurgical properties is paramount. By optimizing grain structures and relieving stresses, these furnaces produce materials with enhanced formability, strength, and surface quality, essential for applications like automotive body panels or precision aerospace parts.
Cost Efficiency
The use of natural gas as a fuel source reduces energy costs compared to electric furnaces, particularly for large-scale operations. Yinuo’s furnaces are designed for high throughput, enabling manufacturers to process significant volumes efficiently, further driving down production costs.
Environmental Responsibility
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of our designs. Low-NOx burners, optimized combustion, and heat recovery systems minimize greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals and helping manufacturers meet regulatory requirements.
Operational Flexibility
Our furnaces are customizable for various annealing processes, material types, and production scales. Whether annealing thin steel strips or heavy aerospace components, Yinuo’s solutions deliver tailored performance. To discuss how we can meet your specific needs, contact us.
Applications Across Key Industries
Gas fired annealing furnaces are indispensable in industries that demand high-quality, processed metals. Their versatility and precision make them a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Steel Production
In steel manufacturing, these furnaces anneal cold-rolled coils and sheets, enhancing formability and surface quality for automotive, appliance, and construction applications. Yinuo’s furnaces ensure uniform properties, meeting the rigorous demands of steel producers.
Aerospace Manufacturing
The aerospace industry relies on gas fired annealing to process alloys for turbine blades, landing gear, and structural components. Precise temperature and atmosphere control ensure materials meet strict standards for strength and fatigue resistance.
Automotive Sector
Automotive manufacturers use annealed steel and aluminum for lightweight, high-strength parts like chassis components and body panels, improving fuel efficiency and crash safety. Our furnaces support high-volume production with consistent results.
Electrical and Energy Applications
In electrical steel production, annealing optimizes magnetic properties for transformers and motors, enhancing energy efficiency. The energy sector also benefits, using annealed components for pipelines and renewable energy systems. Explore our furnace offerings on our Products page.
Yinuo’s Expertise in Furnace Design
At Jiangsu Yinuo Thermal Energy Technology Co., Ltd., we bring decades of experience and innovation to the design and manufacture of gas fired annealing furnaces. Our commitment to precision engineering ensures reliable performance under demanding conditions.
Cutting-Edge Engineering
Our furnaces feature advanced control systems for precise temperature regulation and robust refractory linings for durability. These elements ensure long-term reliability in high-throughput environments.
Tailored Solutions
Customization is at the heart of our approach. We collaborate with clients to design furnaces that align with their unique production goals, from compact batch systems to large-scale continuous lines.
Sustainability Commitment
Sustainability drives our designs. Energy-saving features like low-emission burners and heat recovery systems reduce environmental impact while lowering operating costs.
Comprehensive Support
From installation and operator training to ongoing maintenance, Yinuo provides end-to-end support to ensure peak furnace performance. Learn more about our services on our Services page.
Addressing Operational Challenges
Gas fired annealing furnaces face operational challenges that require sophisticated engineering to overcome, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
Uneven heating can result in inconsistent material properties, compromising quality. Yinuo’s furnaces use multi-zone burners and advanced airflow designs to ensure uniform heat distribution across the chamber.
Controlling Furnace Atmosphere
Preventing oxidation during annealing requires precise atmosphere management. Our furnaces employ automated gas injection systems to maintain protective environments, such as nitrogen or hydrogen-based atmospheres.
Reducing Maintenance Downtime
High-throughput operations demand minimal interruptions. Yinuo’s durable designs and predictive maintenance tools, including thermal imaging and sensor-based diagnostics, extend equipment lifespan and minimize downtime.
These solutions ensure our furnaces deliver reliable, high-quality results in even the most demanding applications.
The Future of Gas Fired Annealing Furnaces
As industries evolve, gas fired annealing furnaces are poised to play a pivotal role in meeting new challenges and opportunities.
Digital Transformation
The integration of IoT and AI is revolutionizing furnace operations. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven optimization reduce downtime and enhance efficiency. Yinuo is incorporating these smart technologies to keep clients at the forefront of innovation.
Cleaner Combustion Technologies
Advancements in burner technology and alternative fuels, such as hydrogen or biogas blends, are reducing emissions. Yinuo is exploring these solutions to support global decarbonization efforts while maintaining performance.
Processing Advanced Materials
The rise of new alloys and composites requires furnaces capable of complex annealing profiles. Our R&D team is developing systems to handle these next-generation materials, ensuring clients remain competitive in rapidly changing markets.
Why Partner with Yinuo?
Jiangsu Yinuo Thermal Energy Technology Co., Ltd. is more than a furnace manufacturer—we are a trusted partner dedicated to your success. Industrial engineers, maintenance technicians, and procurement managers choose Yinuo for several reasons.
Proven Expertise
Our furnaces meet the highest industry standards, delivering reliable performance and long-term value.
Customized Designs
We tailor furnaces to your specific production needs, ensuring optimal efficiency and return on investment.
Global Reach
Our worldwide presence enables us to deliver dependable solutions for industries like steel, aerospace, and automotive.
Customer-Centric Approach
We prioritize your needs, providing support from design to after-sales service to ensure your success.
Ready to enhance your annealing process with a state-of-the-art gas fired furnace? Contact us to schedule a consultation with our team.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gas Fired Annealing Furnaces
What types of materials can gas fired annealing furnaces process?
Our furnaces handle steel, aluminum, copper, and specialty alloys. Yinuo customizes systems to meet specific material requirements.
How do gas fired furnaces compare to electric furnaces?
Gas fired furnaces offer lower operational costs for large-scale processes due to the cost-effectiveness of natural gas. Yinuo’s designs maximize energy efficiency for both.
What environmental benefits do Yinuo’s furnaces provide?
Low-NOx burners, optimized combustion, and heat recovery systems reduce emissions and fuel consumption, supporting sustainability and regulatory compliance.
How does Yinuo ensure consistent annealing results?
Multi-zone burners, smart control systems, and precise atmosphere management maintain uniform heating and material quality.
Are Yinuo’s furnaces suitable for small-scale operations?
Yes, we offer both batch and continuous furnaces, customizable for small to large production scales. Contact us to discuss your needs.
What maintenance support does Yinuo offer?
We provide installation, training, and predictive maintenance with advanced diagnostics to minimize downtime. Visit our Services page for details.
Conclusion
Gas fired annealing furnaces are transformative technologies that enable manufacturers to produce high-quality, reliable materials for the world’s most demanding industries. At Jiangsu Yinuo Thermal Energy Technology Co., Ltd., we lead the industry with innovative furnaces that deliver precision, efficiency, and sustainability. Our customized solutions and comprehensive support empower clients in steel, aerospace, automotive, and beyond to achieve unparalleled results.
Discover our cutting-edge furnace solutions on our Products page. For personalized guidance or to request a quote, visit our Contact page. Partner with Yinuo to unlock the full potential of your manufacturing process with our advanced gas fired annealing furnaces.







